With the increasing popularity of Linux over the years, and the various Linux distributions that are constantly being released, it can be hard to choose the correct one for you. Because Linux is open source, and is not overseen by a specific vendor, knowing and picking the correct distribution can be challenging, however, no matter your requirements, you are bound to find a Linux distribution that suits your needs.
In this guide, we will explore Rocky Linux, why it is starting to become a good choice for enterprises, and how to get an image running on a virtual machine.
What is Rocky Linux?
 Rocky Linux is a free linux distribution, forked off from CentOS, with the intention to eventually replace CentOS when Red Hat decided to step away from it. It is compatible with the RHEL operating system source code which makes it an ideal operating system for many use cases. Being that it is 100% compatible with Enterprise Linux, it makes it kind of a simple, drag and drop-in solution. Furthermore, not only is it very stable and user-friendly, but it is also a perfect choice for your servers and desktop applications. Being that a lot of administrators widely use CentOS and have been looking for a workaround ever since RedHat discontinued support, Rocky Linux was and is the perfect choice. The Co-Founder of CentOS is also the founder of Rocky Linux so with high promise and potential, not only did he try to create something sustainable and something to replace CentOS, but he also created something that could tackle the issues of CentOS. The result: an operating system with high functionality, great security, and very adaptable to any situation.
Rocky Linux is a free linux distribution, forked off from CentOS, with the intention to eventually replace CentOS when Red Hat decided to step away from it. It is compatible with the RHEL operating system source code which makes it an ideal operating system for many use cases. Being that it is 100% compatible with Enterprise Linux, it makes it kind of a simple, drag and drop-in solution. Furthermore, not only is it very stable and user-friendly, but it is also a perfect choice for your servers and desktop applications. Being that a lot of administrators widely use CentOS and have been looking for a workaround ever since RedHat discontinued support, Rocky Linux was and is the perfect choice. The Co-Founder of CentOS is also the founder of Rocky Linux so with high promise and potential, not only did he try to create something sustainable and something to replace CentOS, but he also created something that could tackle the issues of CentOS. The result: an operating system with high functionality, great security, and very adaptable to any situation.
How Does It Compare to Its Predecessor, centOS?
 The single most essential feature of CentOS for users was its binary compatibility with RHEL. CentOS featured all of the features that made RHEL the leading enterprise-class Linux. If you wanted to run industry standard technology without having to deal with corporate, CentOS was the man for the job! However, just as quickly as CentOS rose, it quickly fell. Red Hat discontinued support for CentOS leaving users and companies alike with no replacement. Following the demise of CentOS, Rocky Linux has received widespread adoption and community support, and its future seems quite promising. It runs well as a server since it is built on RHEL's reliable source code, and it can thus be utilized to power multiple production workloads. When Red Hat changed the relationship between future development by Fedora to development for CentOS, it was no longer a stable version of RHEL. Rocky Linux on the other hand was built to be a better, more stable version of RHEL and CentOS, whilst still running off the RHEL binaries. To say the least, ever since its release, Rocky Linux has then grown to one of the biggest distributions today.
The single most essential feature of CentOS for users was its binary compatibility with RHEL. CentOS featured all of the features that made RHEL the leading enterprise-class Linux. If you wanted to run industry standard technology without having to deal with corporate, CentOS was the man for the job! However, just as quickly as CentOS rose, it quickly fell. Red Hat discontinued support for CentOS leaving users and companies alike with no replacement. Following the demise of CentOS, Rocky Linux has received widespread adoption and community support, and its future seems quite promising. It runs well as a server since it is built on RHEL's reliable source code, and it can thus be utilized to power multiple production workloads. When Red Hat changed the relationship between future development by Fedora to development for CentOS, it was no longer a stable version of RHEL. Rocky Linux on the other hand was built to be a better, more stable version of RHEL and CentOS, whilst still running off the RHEL binaries. To say the least, ever since its release, Rocky Linux has then grown to one of the biggest distributions today.
Pros of Rocky Linux
Compatibility
Rocky Linux's compatibility with Red Hat Enterprise binaries increases efficiency and reassures many customers about the distribution's performance. Moreover, Rocky Linux makes it easy to migrate from CentOS, Alma Linux and other distributions using one tool. Rocky Linux also has fixed Cloud apps and container images being used without issue.
Open Source
The fact that Rocky Linux is open source is one of its most notable features, which has helped to create a sizable and cohesive support community for it. Uninterrupted and free from any obstacles, it can offer a variety of updates to meet user needs and offer a full level of security, giving users hope for a successful future for Rocky Linux as a desirable replacement for its precursor.
Stability
Since Rocky Linux was developed to take the position of CentOS, it should emphasize the stability of CentOS as its key characteristic and perform flawlessly in this area to win over people. As a result, Rocky Linux prioritizes system reliability despite systems with recent updates and instability.
Support
Before the release of Rocky Linux, the developer was aware of the requirements of CentOS users and the useful features of CentOS that were crucial for its users, so he made the decision to stick with the open-source path and establish a sizable and potent support community so that users could choose this distribution for their activities without any concern.
Cons of Rocky Linux
Still too soon
Although the operating system is still in its early stages, future plans are already being prepared. The frequency of updates will depend on how dedicated the community is and how strong the financial support is. Currently, several major corporations serve as sponsors. How long this assistance will really be provided, though, is unclear.
Updates
It always takes time for new apps to get live. Rocky Linux, the CentOS replacement, has up to this point operated extremely steadily on every server, much like CentOS. However, since rolling releases and regular updates are the norm here, you will probably choose CentOS Stream if you always want to have the most recent version of the operating system. Rocky Linux operates substantially more slowly in contrast. Users that appreciate durability will find the system more suited as well as developers who want a distro that releases updates constantly.
Is Rocky Linux Secure?
 One of the primary goals when creating Rocky Linux was to maintain stability whilst also being secure at the enterprise level. Now, with the release of Rocky Linux 9 not too long ago, we have received just that. Below are just a few of the security features that were implemented:
One of the primary goals when creating Rocky Linux was to maintain stability whilst also being secure at the enterprise level. Now, with the release of Rocky Linux 9 not too long ago, we have received just that. Below are just a few of the security features that were implemented:
- Since the cryptographic hash functions generated by SHA-1 are no longer regarded as secure, the use of SHA-1 message digests for cryptographic purposes has been discouraged.
- OpenSSL has significant enhancements in version 3.0.1, including support for additional protocols, formats, algorithms, and more. Other changes include a provider concept, a new versioning system, an enhanced HTTP(S) client, and more.
- The most notable change in OpenSSH 8.7p1 is the substitution of the SFTP protocol for the SCP/RCP protocol, which provides more predictable filename processing.
- Significant improvements have been made to SELinux speed, memory overhead, load time, and other factors.
Moreover, being that Rocky Linux heavily relies on released security package updates from RHEL, it is safe to say that it will continue to remain secure.
How To Install Rocky Linux
When it comes to installing Rocky Linux, you can either opt for Rocky Linux 8 or Rocky Linux 9, RL9 being the latter rather than the former. Although RL8 is still very usable, there are notable differences between the two versions. In comparison to RHEL and RL8, Rocky Linux 9 now ships with Apache HTTP Server 2.4.51 and nginx 1.20 support, support for MariaDB 10.5, MySQL 8.0, PostgreSQL 13, and Redis 6.2, support for Varnish Cache 6.6 and Squid 5.2 as proxy caching servers, new versions of popular dynamic programming languages such as Node.js 16, Perl 5.32, PHP 8.0, Python 3.9, and Ruby 3.0, and support for OpenSSL 3.0.1, OpenSSH 8.7.01, and automatically configured compliance settings for PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and DISA. With that being said, let's get into the install!
The most recent download link for Rocky Linux can be found download, as well as different architectures, different ISOs whether it be DVD, minimal, boot, or torrent, and finally, you can find a checksum of said downloaded file to confirm the integrity of the download beforehand. If you are on a Linux system, you can run the command below to download using wget:
|
wget |
Once downloaded, if you’d like to perform a checksum, you can run the following command below:
|
wget |
Afterwards, you should have a checksum file called CHECKSUM in the respective directory. Run the command below to confirm the checksum:
|
sha256sum -c CHECKSUM --ignore-missing |
If everything is successful, you should be greeted with the following message:
|
Rocky-9.0-x86_64-minimal.iso: OK |
Depending on the ISO you used, the name will vary e.g x86_64-minimal.iso, x86_64-boot.iso, or x86_64-DVD.iso. Once done, we can move ahead with the installation. For many use cases, you will find yourself creating a bootable USB unless you are using a software such as VirtualBox or VMWare. For this example, we will be using VirtualBox to simulate one possible use case.
Virtual Box Setup
Step 1: Assign a name
Step 2: Configure Machine Settings
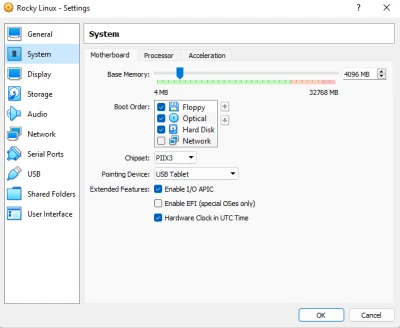
Here we are configuring the “Motherboard” so to speak. Here you can configure the amount of RAM, the boot order, chipset, so on and so forth. For the boot order, you want to have the floppy/optical options first to load our OS onto the Virtual Hard Drive. After installation, we then put the Hard Disk as the first option.
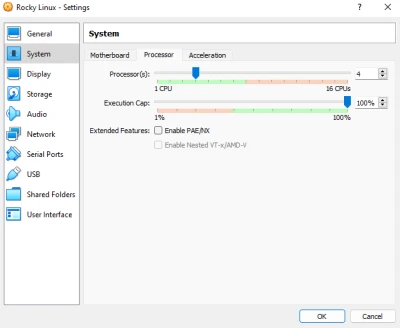
Here, we are configuring the processor(s) and execution cap. At an enterprise level, if you plan to use the virtual machine for intensive loads, then a higher processor amount will most likely be needed.
Step 3: Configuring Storage
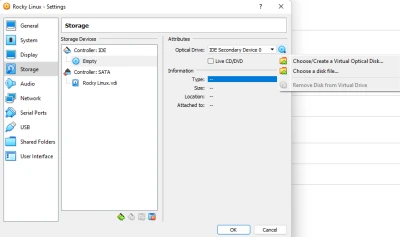
Here we are configuring the Optical Drive which is used to load the ISO file onto the virtual machine. Make sure to click on “Choose a disk file…” from the dropdown menu after clicking the blue CD icon. Afterwards, it should look something like this:
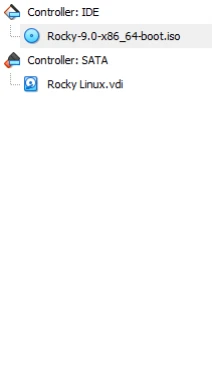
Step 4: Configure Network Settings
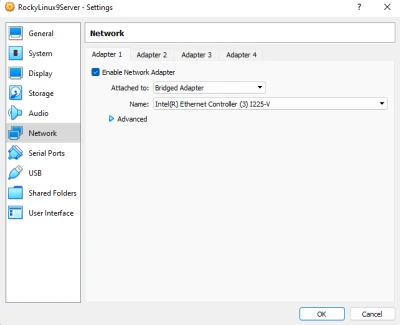
Here we are configuring the network settings. Depending on how you would like to use Rocky Linux, and considering you have the hardware to support these virtual machines such as a rack, you might want to bridge this to your network. Things such as DNS servers, DHCP servers, etc require this to be bridged rather than using something like NAT.
Installation:
Once everything is set up properly, we can launch up our virtual machine. After doing so, you should be greeted with this screen:
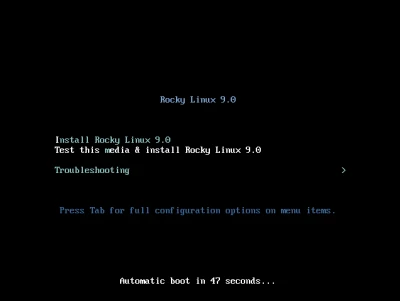
For this instance, we will be selecting the second option. After selecting that, you will be greeted with a welcome screen like below:
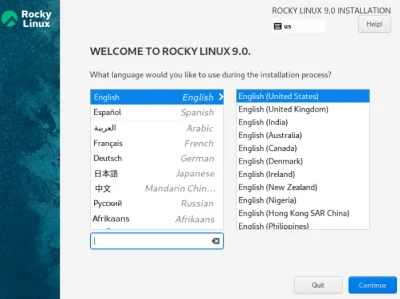
Here, we select the language that we want our server to run.
Here, you can configure a couple of things. Firstly, we can configure network settings like below:
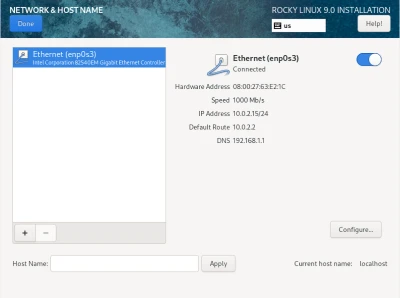
We can also configure security settings and profiles. The great thing about Rocky Linux is that they have pre-made and pre-configured security profiles that you can choose from. They range from low-level security to enterprise-grade fortress-like security. For this instance, we used a very low-level security profile.
We can also configure storage settings and create partitions as needed, however, for this instance I will be using the standard configuration.
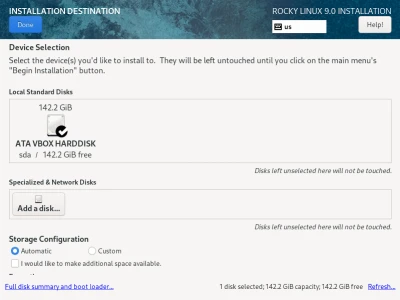
We can also choose how we want to set up our instance of RL9 (base environment) as well as any software such as making RL9 a DNS server or DHCP server.
After going through everything and the install finishes, you will be prompted to reboot your system:
After you reboot your machine, you should be greeted with the following screen below:
Here, we select the first option and it should take us to this screen:
When you get to this screen, just click on start setup. One of the reasons why RL9 is so popular is for its ability to make a Linux server operate with a GUI, plus it being completely open-source, hence FREE! After you click on that button, you should see this screen
Here, we can connect any accounts that we may have. After doing this step, or skipping it, you should see this as shown below:
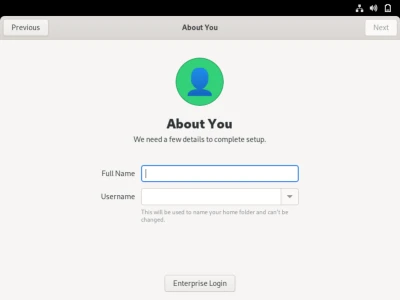
This is the account creation process. You first input your name and username as shown above and you will then be greeted by the screen below:
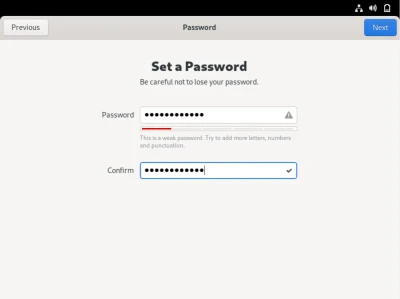
Here you will set a password. For this instance, I set a low-security password that could probably be cracked. Our suggestion would be to use randomized passwords or something big in length with a mixture of lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters. After that, we should finally be at this screen as shown below:
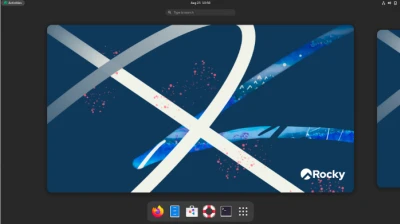
Finally, we have installed RL9! Depending on how you set up your instance, you may have different tools, settings, and security configurations however, this is the general greeting screen you will see. The reason why RL9 is such a game changer is because they’ve basically provided administrators with a fully capable, enterprise-level distribution of linux that is full GUI. Tools such as DHCP set up, DNS set up, and so forth are all within a GUI. It is essentially the windows server of linux so to speak. Rocky Linux 9 is not only ready for high, operation-intensive enterprises, but it is doing so in style making it easier for administrators.
Final Thoughts
There is a distinction between a Linux workstation and a server. The distribution you choose may have an impact on the performance of your server which is why it is critical to select the appropriate Linux distribution for your needs. For the same reason, this is why Rocky Linux is a gift to many Linux users and admins alike who grieve the loss of CentOS 8.0 and are not fans of Fedora. Users and admins migrating from CentOS to Rocky Linux will be pleasantly pleased by the distributions familiar appearance and feel. Moreover, Rocky Linux is very easy to navigate and traverse for new Linux users making it a great choice for many use cases.